Astro-Mathematics
Iteration
It is often necessary to find the zero value, maximum value, or. minimum value of a function. The function can be very complex. a good example is the position of a planet which is obrtained from complex polynomial expansions. Iteration is the only effective means of obtaining the required result.
Golden Section Search
The golden section search is an effective means of determine the maximum or minimum of a function \(f(x)\). We will start with the minimum.
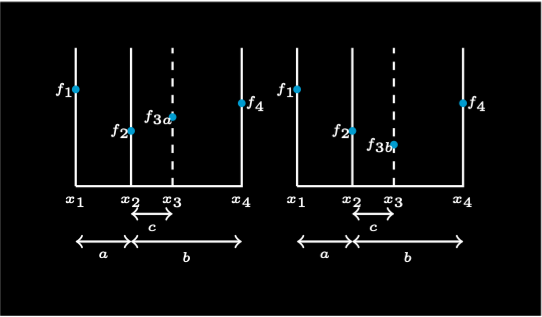
[ps] shows how the golden section search works. The initial conditions are triplet \(x_1,x_2,x_4\) where \(f(x_1) < f(x_2) < f(x_4)\). The minimum is in the interval \((x_1, x_4)\). We need to find the value of \(x_3\) with function values \(f_{3a}\) or \(f_{3b}\).
There are the three distances \(a = x_2 - x_1\), \(b = x_4 - x_2\), and \(c = x_3 - x_2\).
If, as in the left diagram, \(f(x_1) < f(x_2) < f(x_{3a})\), then the new triplet will be \(x_1,x_2,x_3\). We want the new triplet spacing to be the same as the original.
Reorganise.
If, as in the right diagram, \(f(x_2) < f(x_{3b}) < f(x_4)\), then the new triplet will be \(x_2,x_3,x_4\). Again, we want the new triplet spacing to be the same as the original.
Multiply by denominators \(b(b - c)\).
Reorganise.
Eliminate \(c\).
Divide by \(a\) and multiply by \(b(a + b)\).
Divide by \(a^2\).
Rearrange and complete the square.
This gives:
Where \(\phi\) is the golden ratio.
We need to calculate the value \(r = a + c\) such that \(x_2 = x_4 - r\) and \(x_3 = x_1 + r\).
This is an important result. We only needed the value of \(x_2\) for the proof. We now know that we can calculate the values of \(x_2\) and \(x_3\) from \(x_1\), \(x_4\), and \(\phi\)!
Golden Section Search Algorithm
Given that we have a triplet \(x_1, x_2, x_4\) where \(f(x_1) > f(x_2) < f(x_4)\) for a minimum or \(f(x_1) < f(x_2) > f(x_4)\) for a maximum and a tolerance \(\delta\). We can discard the value of \(x_2\) and the function values as they are no longer needed.
-
Calculate the ratio \(r = (x_4 - x_1)/\phi\).
-
Set \(x_2 = x_4 - r\) and calculate \(f_2 = f(x_2)\).
-
Set \(x_3 = x_1 + r\) and calculate \(f_3 = f(x_3)\).
-
If \(f_2 < f_3\) for a minimum or \(f_2 > f_3\) for a maximum set \(x_4 = x_3\).
-
Othersise set \(x_1 = x_2\).
-
If \(x_4 - x_1 > \delta\) go to step 1.
-
Return \((x_1 + x_4)/2\).
